Hypothyroidism is a common endocrine disorder characterized by an underactive thyroid gland, which fails to produce sufficient thyroid hormones. These hormones play a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development throughout the body.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
The symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary widely and may develop slowly over time, making them difficult to recognize. Common signs and symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, constipation, feeling cold, muscle weakness, depression, and cognitive difficulties.
Other manifestations may include hair loss, brittle nails, menstrual irregularities, and a hoarse voice.
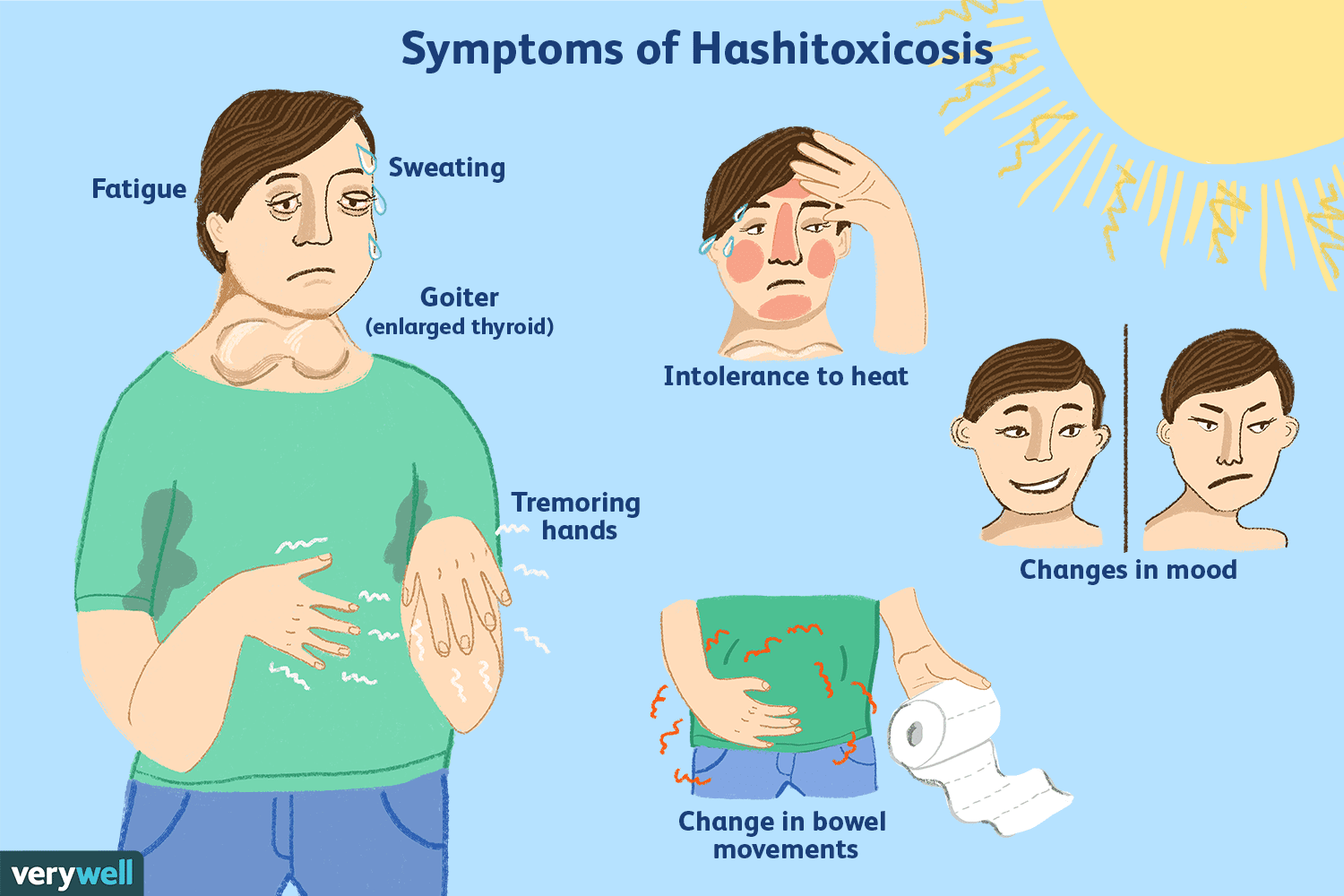
However, it’s important to note that symptoms can vary among individuals, and some people may experience only a few or even no noticeable symptoms.
Diagnosing Hypothyroidism
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and blood tests to measure thyroid hormone levels. The primary hormone measured is thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is produced by the pituitary gland and stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Elevated TSH levels, along with low levels of T3 and T4, indicate hypothyroidism. Additional tests, such as thyroid antibody tests, may be performed to determine the underlying cause of the condition.
Treatment Options for Hypothyroidism
The primary treatment for hypothyroidism involves replacing the deficient thyroid hormones through thyroid hormone replacement therapy. The most commonly prescribed medication is synthetic levothyroxine, which is identical to the body’s natural T4 hormone.
The dosage is adjusted individually based on the patient’s hormone levels and response to treatment. Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels is necessary to ensure the appropriate dosage and to optimize the therapeutic effects.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications can also play a role in managing hypothyroidism. These include maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and other essential nutrients, as deficiencies in these elements can contribute to thyroid dysfunction.
Regular exercise can help boost metabolism and alleviate symptoms such as fatigue and weight gain.